the impact of inpatient point-of-care blood glucose quality control testing|Clinical Reliability of Point : distribution Glycemic control in hospitalized patients with diabetes requires accurate near-patient glucose monitoring systems. In the past decade, point-of-care blood glucose monitoring devices have . Resultado da Análise + bônus 2024. Matheus Bastos. 07/02/2024. 10:40. No mundo dos melhores cassinos online, a confiança é essencial para os jogadores. E o Spin Casino se destaca como uma plataforma de renome, reconhecida por sua qualidade e integridade. Se você está se perguntando se vale a pena .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web5 de fev. de 2024 · NumPy is a community-driven open source project developed by a diverse group of contributors. The NumPy leadership has made a strong commitment to creating an open, inclusive, and positive community. . Download files. Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
What We Should Consider in Point of Care Blood Glucose Test; C
Analyze the effectiveness of mandated point-of-care (POC) blood glucose (BG) meter quality control (QC) testing. All POC BG QC tests were analyzed to evaluate operator and strip/meter error rates and institutional cost.Glycemic control in hospitalized patients with diabetes requires accurate near . Point-of-care blood glucose monitoring devices have become the mainstay of near-patient glucose monitoring in hospitals across the world and their clinical value for .
Glycemic control in hospitalized patients with diabetes requires accurate near-patient glucose monitoring systems. In the past decade, point-of-care blood glucose monitoring devices have . This website requires cookies, and the limited processing of your personal data in order to function. By using the site you are agreeing to this as outlined in our privacy notice .
drop test mil-std-810g
Analyze the effectiveness of mandated point-of-care (POC) blood glucose (BG) meter quality control (QC) testing. All POC BG QC tests were analyzed to evaluate operator and strip/meter error rates and institutional cost. Analyze the effectiveness of mandated point-of-care (POC) blood glucose (BG) meter quality control (QC) testing. All POC BG QC tests were analyzed to evaluate operator and.
While POCT for BG has become the mainstay for monitoring and decision making in the management of diabetes in inpatients, it cannot replace CLT for precision and accuracy. Point-of-care glucose testing is user friendly . This study directly compared POC capillary glucose values to venous glucose values in our facility’s ICU population in order to assess the clinical reliability of POC glucose . Critically ill patients require frequent, accurate blood glucose (BG) monitoring. BG measurement devices and sample types have significant differences related to cost, .
POCT can quickly report results, which can be quickly applied to diagnosis and treatment of patients, contribute to improved patient satisfaction by reducing blood sample volume, and . Quality control testing verifies that an . 21. Corl DE, Yin TS, Hoofnagle AN, Whitney JD, Hirsch IB, Wisse BE. The impact of inpatient point-of-care blood glucose quality control testing. J . Tran NK, Godwin ZR, Bockhold JC, Passerini AG, Cheng J, Ingemason M. Clinical impact of sample interference on intensive insulin therapy in severely . In the United States, the annual estimated cost of treating diabetes in 2012 was 5 billion, a 41% increase from 2007. The largest component (43%) related to inpatient care. 1 A 5-country EU study estimated that in . Blood glucose meters: point-of-care testing. PDF, 190 KB, 4 pages. This file may not be suitable for users of assistive technology. . quality control and assessment; record keeping;
Two widely accepted standards for blood glucose meters ISO 15197:2013 (for self-monitoring) and USFDA Prescription Point-of-Care Use (for hospital use) were adopted to evaluate the accuracy.
In the past decade there has been a rapid increase in the scope and frequency of point-of-care testing (POCT), whereby a diagnostic test – such as blood glucose measurement – is carried out in a convenient and timely manner close to the site of patient care, e.g. the hospital bedside. Rajendran, R. & Rayman, G. Point-of-Care Blood Glucose Testing for Diabetes Care in Hospitalized Patients: An Evidence-Based Review. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 8 , 1081–1090 (2014). Inaccuracy of glucose monitoring may derive from test strip, patient, pharmacological, environmental, and other factors. 1 Incorrect results may cause serious harm and change clinical decisions. 2,3 To ensure reliable results, POC devices and test strips should be stored and operated according to manufacturer specifications. In tropical settings, .QC Explained 1. 0 - Quality Control for Point of Care Testing 3 1.0 Importance of Quality Control for POCT Devices ISO 15189 states that “Quality Control materials shall be periodically examined with a frequency that is based on the stability of the procedure and the risk of harm to the patient from an erroneous result” (1). Therefore, when
While most laboratory testing continued to be performed in the main clinical laboratory, arterial blood gases, electrolytes, glucose, urine analysis were performed in wards and critical care areas without central laboratory supervision, report generation, lack of training and lack of evidence of quality control.Rajendran R, Rayman G, et al. Point-of-care blood glucose testing for diabetes care in hospitalized patients. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2014;8:1081-1090. Tran NK, Godwin ZR, Steele AN, et al. Clinical Impact of Accurate Point-of-Care Glucose Monitoring for Tight Glycemic Control in Severely Burned Children. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2016;17:e406-e412. A1C reflects average glycemia over approximately 3 months. The performance of the test is generally excellent for National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program (NGSP)-certified assays (see www.ngsp.org).The test is the major tool for assessing glycemic control and has strong predictive value for diabetes complications (1–3).Thus, A1C testing should be .
The Impact of Inpatient Point-Of-Care Blood Glucose Quality Control Testing Dawn E. Corl, Tom S. Yin, Andrew N. Hoofnagle, JoAnne D. Whitney, Irl B. Hirsch, Brent E. Wisse The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) regulates all U.S. laboratory testing except research through the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) program. 7 The purpose of this program is to ensure quality laboratory testing. POC blood glucose testing in hospitals is under the purview of CMS.
What We Should Consider in Point of Care Blood Glucose Test;
The impact of inpatient point
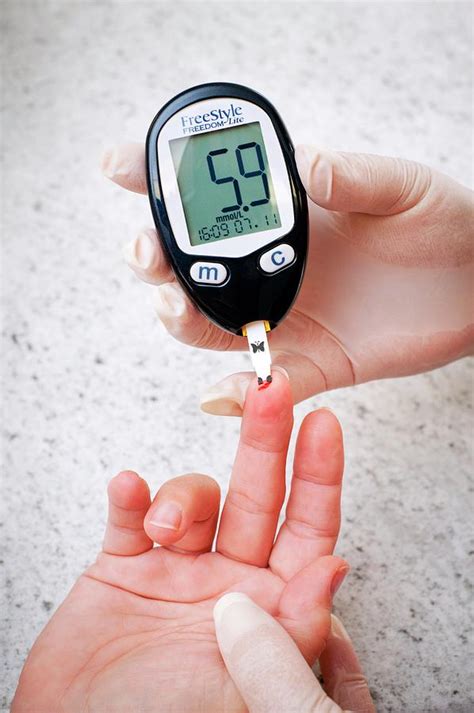
Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Point-of-Care Capillary Blood Glucose Monitoring. POC glucose monitoring was performed before meals and at 2 h after meals, at bedtime, and at 3 am starting on admission to the hospital. The glucometer used was from Abbott (FreeStyle Precision Pro, Alameda, CA).
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology in the outpatient setting has transformed glucose monitoring for diabetes self-management, providing more comprehensive glycemic control data than intermittent point . Background: Blood glucose measurement is a way of monitoring changes in glycaemia. Different point-of-care testing (POCT) glucose meters are on the market and hence there is an increase in .Rapid point-of-care testing for quick decisions on diabetes. Diabetes is one of the biggest global public health concerns and continues to rise in prevalence. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF), says that, as of 2021, 537 million adults 20-79 years old are living with diabetes worldwide. That’s the same as 1 in 10 people. For appropriate glycemic control in clients with diabetes mellitus in non-critical care settings, capillary blood glucose testing is the recommended testing method. Blood glucose testing is recommended before meals and bedtime for clients who can eat. Clients receiving enteral feeds or are nil by oris (NPO) should be tested every 4 to 6 hours.
16.1 Perform an A1C test on all people with diabetes or hyperglycemia (random blood glucose >140 mg/dL [>7.8 mmol/L]) admitted to the hospital if no A1C test result is available from the prior 3 months.B. 16.2 Institutions should implement protocols using validated written or computerized provider order entry sets for management of dysglycemia in the .Analyze the effectiveness of mandated point-of-care (POC) blood glucose (BG) meter quality control
Abstract Analyze the effectiveness of mandated point‐of‐care (POC) blood glucose (BG) meter quality control (QC) testing. All POC BG QC tests were analyzed to evaluate operator and strip/meter erro.Lewandrowski K, Cheek R, Nathan DM, et al. Implementation of capillary blood glucose monitoring in a teaching hospital and determination of program requirements to maintain quality testing. Am J Med 1992;93:419–26. Rumley AG. Improving the quality of near-patient blood glucose measurement. Ann Clin Biochem 1997;34(Pt 3):281–6. Boyd JC .
In the United States, the annual estimated cost of treating diabetes in 2012 was 5 billion, a 41% increase from 2007. The largest component (43%) related to inpatient care. 1 A 5-country EU study estimated that in 2010, the total direct costs of care for people with diabetes were highest in Germany (in part due to the greater diabetes population) at €43.2 .POC-BG data captured through automated data management software can support hospital efforts to monitor the status of inpatient glycemic control and facilitate the creation of a national benchmarking process for the development of best practices and improved inpatient hyperglycemia management. BACKGROUND Despite increased awareness of the value of .
Training Materials. Infection Prevention in Point of Care Testing: This PowerPoint presentation touches on key infection prevention issues in the use of point of care testing and may be revised as desired to support the educational needs of the individual center. Preventing Infection During Blood Glucose Monitoring and Insulin Administration (OPSC): This 10-minute video from the . Glucose control in the hospital setting is very important. There is a high incidence of hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability in hospitalized patients. Safe insulin delivery and glucose control is dependent on reliable glucose meters and monitoring systems in the hospital. Different glucose monitoring systems use arterial, venous, central venous, and .
Extensive evidence has associated inpatient hyperglycemia with poor clinical outcomes in patients with and without diabetes (1–3).Several randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses have demonstrated that basal-bolus insulin therapy improves glycemic control and clinical outcomes in non–critically ill hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) ().
drop test military standard hardrive
Resultado da Dra Rafaela Batisti Nery, Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro. 100 likes. Medicina Reprodutiva de Forma Leve/ Descontraída com Poesia e Arte RQE 37289 e 37299 WhatsApp p/ .
the impact of inpatient point-of-care blood glucose quality control testing|Clinical Reliability of Point